Table of Contents
Catamenial pneumothorax: Presentation of an uncommon Pathology
Published on: 20th December, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317596988
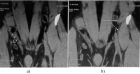
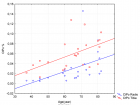
The catamenial pneumothorax is defined as the accumulation of air in the pleural cavity that appears in women infrequently and spontaneously with various clinical presentations. Actually, it is considered as an extremely rare entity with few cases described in the literature, that is the reason why the etiology is still discussed. However, a strong association with thoracic endometriosis syndrome has been found. We want to emphasize how the importance of conducting a diagnosis and having a timely management would improve the quality of life of the patient and give a better prognosis of the disease. Thus, a case report of a 38-year-old female patient who was receiving hormone therapy as a treatment for abdominal endometriosis and repetitive pneumothorax was presented. In the video-assisted thoracoscopy we saw diaphragmatic lesions and pneumothorax during the perioperative and postoperative period. Emphasize the importance of a detailed inspection of each intrathoracic organ during the surgical procedure, we also showed how the intraoperative pleurodesis, the placement of a mesh on the diaphragm and the continuity of the hormonal treatment, seems to be an effective therapy to prevent recurrences and have a better control of the disease.
Giant Lipoma Anterior Neck: A case report
Published on: 14th December, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8465495935
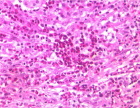
Lipoma is a benign mesenchymal tumor with a thirteen percent incidence in head and neck region. Posterior triangle is the most common location while anterior neck lipoma is a rare one. Giant lipomas >10cm have been reported in different parts of the body but rarely in the anterior neck. Giant lipomas of the neck can present as a cosmetic disfigurement or can produce pressure symptoms. Most lipomas do not pose any difficulty in diagnosis. Surgical excision remains the treatment of choice. We here present a case of giant anterior neck lipoma.
Gastric Mucosal Calcinosis
Published on: 27th September, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317601908
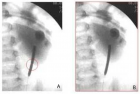
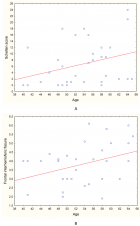
Gastric mucosal calcinosis is a very rare pathology of the gastric mucosa. It may develop secondary to several diseases but may also be idiopathic in some cases. In this case, gastric mucosal calcinosis was diagnosed with endoscopic biopsy performed for a patient who presented to our clinic with heartburn and abdominal discomfort. This case involves a very rare gastric pathology, and is being studied here with reference to literature data.
Trichomonas Vaginalis-A Clinical Image
Published on: 21st July, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317592100
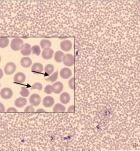
A 32-year-old G4P301LC3 woman presents to the office for a visit, with a 6-day history of vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. On speculum examination, the discharge was green in color and frothy in appearance. Is noticed vulvar erythema, edema, and pruritus, also is noted the characteristic erythematous, punctate epithelial papillae or “strawberry” appearance of the cervix. Vaginal pH was 6.2. Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis is made via wet prep microscopic examination of vaginal swabs.But also, for diagnosis help even the exam with the speculum, concretely “strawberry” appearance of the cervix. The diagnosis is confirmed by culture.Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection [1,2], that caused by trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginalis is a unicellular, anaerobic flagellated protozoan, that inhabits the lower genitourinary tracts of women and men, but that can cause vaginitis. Clinical findings of Trichomonas vaginalis include a profuse discharge with an unpleasant odor. The discharge may be yellow, gray, or green in color and may be frothy in appearance. Vaginal pH is in the 6 to 7.Vulvar erythema, edema, and pruritus can also be noted. The characteristic erythematous, punctate epithelial papillae or “strawberry” appearance of the cervix is apparent in only 10% of cases. Symptoms are usually worse immediately after menses because of the transient increase in vaginal pH at that time. Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis is made via wet prep microscopic examination of vaginal swabs. Other, more sensitive tests are available, including nucleic acid probe study and immunochromatographic capillary flow dipstick technology. The diagnosis can be confirmed when necessary with culture, which is the most sensitive and specific study. Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) have replaced culture as the gold standard. T vaginalis NAATs have been validated in asymptomatic and symptomatic women and are a highly sensitive test [3]. Because the Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection, both partners should be treated to prevent reinfection. The mainstay of treatment for Trichomonas vaginalis infections is metronidazole. Treatment schemes can be:

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."